Taking liquid calcium with red sage can build stronger bones
09/18/2018 / By Michelle Simmons
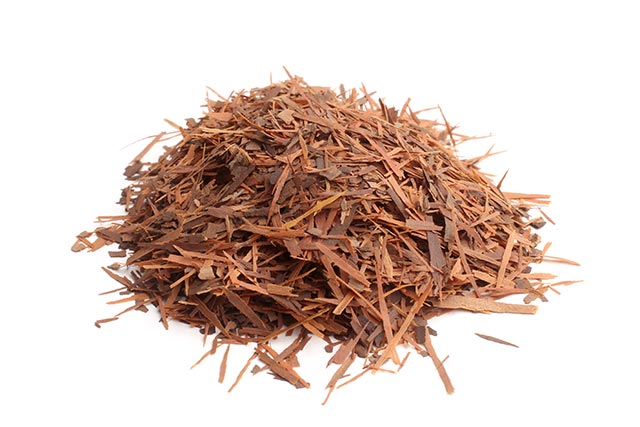
Preventing osteoporosis, especially in postmenopausal women, is possible with the help of this traditional Asian medicine, according to research. A study published in the BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine revealed that taking red sage (Salvia miltiorrhiza) extract with liquid calcium can make the bone stronger and prevent osteoporosis.
Type 1 osteoporosis is most common in postmenopausal women and is associated with an estrogen deficiency. As women age, their ovaries do as well, affecting ovarian function, such as the production of estrogen. On the other hand, type 2 osteoporosis is caused by aging and is mostly due to decreased dietary calcium and vitamin D or increased parathyroid gland activity. (Related: Osteoporosis – This Silent Disease Affects More Than Just Older Women.)
Researchers from Kyung Hee University in Korea aimed to find a natural solution to keep the bones healthy and prevent osteoporosis. In their study, they looked at the protective effects of red sage extracts combined with liquefied calcium supplement against osteoporosis.
For the study, they orally gave ovariectomized mice with different doses of red sage extracts, a combination of red sage extracts and liquefied calcium, or liquid calcium supplement every day for 12 weeks. After the treatment, the mice were subjected to micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) analysis to evaluate structural bone loss.
The micro-CT analysis results revealed that oral treatment of red sage extracts combined with liquid calcium prevented tibial bone loss, sustained trabecular bone state, and improved bone biochemical markers. Moreover, it decreased levels of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL), which plays a role in osteoclast regulation, osteocalcin, and bone alkaline phosphatase (BALP). It also exhibited better protection against estrogen-dependent bone loss compared to red sage extracts and liquefied calcium.
Based on the findings of the study, the researchers concluded that red sage extracts combined with liquid calcium supplement may improve bone mineral density and prevent bone loss due to estrogen deficiency.
Other benefits of red sage
Red sage is known as danshen in Chinese medicine. Red sage is available in various forms: capsules, tincture, and tea. This herb has been used for hundreds of years as a medicine for many health conditions. Here are some of them:
- It supports heart health: Most traditional uses for red sage are related to problems of the heart, according to a study published in the Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine journal. It can help relieve chest pains and is often recommended for angina, myocarditis, and heart attack.
- It helps improve diabetes complications: Some research on red sage suggest that this herb can help prevent secondary complications linked to diabetes, such as diabetic retinopathy or eye disease. Red sage can also help enhance the visual function of people with diabetic retinopathy, according to another study published in the Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine journal.
- It supports liver health: In a study published in the journal Liver International, it was discovered that taking red sage pills effectively regenerated liver in mice. In addition, research has shown that red sage can help treat liver fibrosis, a condition characterized by scar tissue buildup caused by hepatitis B. Scar tissue can prevent blood infusion in the liver, which hardens the cells. A compound in red sage root called salvianolic acid B prevented the production of LX-2 cells that become scar tissue. Researchers of that study suggested that using red sage compounds during the early stages of liver fibrosis could help prevent the condition from getting severe.
- It helps relieve menstrual pain: In China, red sage root has been used to treat menstrual cramps for years.
Read more news stories and studies on preventing bone loss naturally by going to AlternativeMedicine.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, bone health, bone loss, bone mineral density, calcium, danshen, estrogen deficiency, herbal medicine, Herbs, natural cures, natural healing, natural medicine, natural remedies, Naturopathy, nutrients, nutrition, osteoporosis, red sage, supplements