A compound found in goldenseal proven to possess cancer-fighting properties
03/26/2019 / By Michelle Simmons
Scientists continue to search for natural cancer treatments. A team of researchers at Nagasaki International University in Japan found that a natural compound known as berberine can help protect against cancer, particularly leukemia, by inducing cancer cell death.
For the study, the research team looked at the subcellular localization and the apoptotic mechanisms of berberine. They treated human promyelocytic leukemia cells with berberine, then examined the antiproliferative activity of the compound.
The research team found that after five to 15 minutes of treatment, berberine exhibited powerful antiproliferative activity in the cells. Then, the researchers investigated the effect of berberine on inducing cell death and found that the compound induced cell death in leukemia cells.
The findings of the study, which were published in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, suggest that berberine can be used against leukemia as it has the ability to induce cancer cell death.
What you need to know about berberine
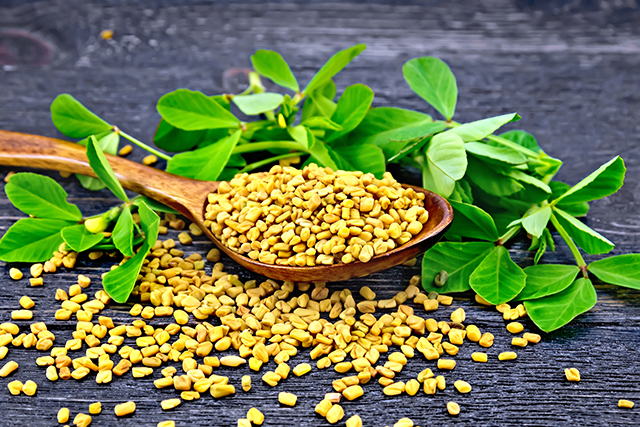
Berberine is an isoquinoline alkaloid used in traditional and folk medicines. It can be found in medicinal plants such as goldenseal and other plants belonging to the Berberis group. Because of its yellow color, it has often been used as a dye. Its medicinal use can be traced back to ancient China, where it was used to treat various health problems. Today, there are already many studies that have confirmed berberine’s benefits for various health problems.
The many health benefits of berberine
In addition to its cancer-fighting properties, here are the other health benefits of berberine supported by scientific studies:
Berberine significantly lowers blood sugar: Various studies have shown that berberine can dramatically reduce blood sugar levels in people with Type 2 diabetes. In fact, it has been found to be as effective as the widely-used diabetes drug called metformin. But of course, berberine is much safer because it is natural. Research has revealed that it works in different ways. It reduces insulin resistance, which makes insulin more effective. It also increases glycolysis, which helps the body break down sugars inside cells. In addition, it reduces the production of sugar in the liver and slows down the breakdown of carbohydrates in the gut. Lastly, berberine increases the number of beneficial bacteria in the gut. (Related: Berberine is a little-known yet powerful supplement that can support gut health and manage blood sugar levels.)
Berberine aids in weight loss: For those who want to lose weight, berberine may be helpful. There are some studies that have examined the effects of berberine on body weight. In one study, obese individuals took 500 milligrams (mg) of berberine thrice a day for 12 weeks and lost five pounds of weight, on average. They also lost 3.6 percent of their body fat. Another study conducted in 37 individuals with metabolic syndrome took 300 mg of berberine thrice a day for three months and experienced significant weight loss. The researchers believe that this effect of berberine on weight loss may be attributed to its ability to improve fat-regulating hormones, such as insulin, adiponectin, and leptin.
Berberine lowers cholesterol: Many studies have shown that berberine can reduce levels of cholesterol and triglycerides, at the same time, increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) or good cholesterol levels. All these factors contribute to the prevention of heart disease.
Preliminary studies have also shown that berberine may have benefits against depression, fatty liver, heart failure, and infections. It also exhibits powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. The common dosage recommendation for berberine supplements is 500 mg, taken thrice a day, 30 minutes before meals. You should take note that it may cause digestive side effects in some people.
Read more news stories and studies on natural treatments for cancer like berberine by going to AntiCancer.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, anticancer, apoptosis, berberine, cancer, cell death, herbal medicine, Herbs, leukemia, medicinal plants, natural cures, natural healing, natural medicine, natural remedies, research



















