Chinese medicine found to help COPD patients strengthen their lungs
08/30/2018 / By Rhonda Johansson
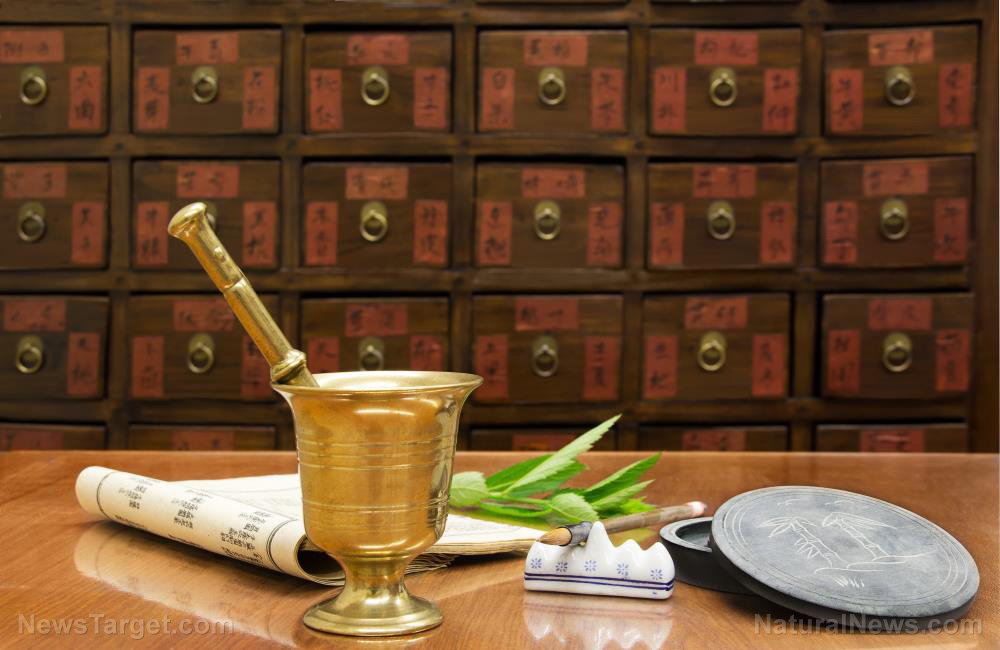

Radix Stemonae is a traditional Chinese remedy used to treat various lung conditions. Its use in Asian ethnomedicine – where it is called bai bu – is based on the tuber’s “warm” properties; that is, it is used to clear “cold” conditions, under which chronic respiratory disorders are usually developed. Bai bu’s popularity has only been increasing in recent years, so much so that scientists have decided to clinically review the plant’s mechanisms of actions in alleviating various symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
In a controlled trial, researchers divided Sprague Dawley rats into three groups: control (that received no treatment nor was subjected to any disease), COPD (in which rats displayed similar characteristics of human COPD patients), and treatment (which received various doses of bai bu extract). The rats were fed a similar diet for 112 days then were sacrificed.
Each rat’s lung function was tested and analyzed, with the right lower lung left fixed for morphologic observation. Inflammatory mediators in serum were observed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
It was found that rats that were given Radix Stemonae were able to keep their healthy weight compared to rats that had COPD. Further, bai bu improved pulmonary function in the rats, with the incidence of inflammation and emphysema being milder than in rats that had COPD.
Authors of the study concluded that a concentrated decoction of Radix Stemonae shows potential in mitigating COPD and improving airway rebuilding in the lungs of affected patients.
These results were published in BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
COPD: A known, but not heavily discussed, disease
Chronic lower respiratory disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). COPD describes a group of diseases that cause blockages in the airway and includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
Symptoms of COPD include shortness of breath, excess phlegm, mucus, or sputum, and frequent coughing or wheezing.
The CDC estimates that around 15.7 million (or around six percent) of Americans have been diagnosed with COPD; although this number might be higher. Roughly half of adults with low pulmonary function are not aware they have the disease.
Those most at risk are:
- Heavy smokers
- The unemployed or those retired or unable to work
- People with a history of asthma
- The elderly
- Women
- Native Americans and multi-racial non-Hispanics
- Those who are newly divorced, widowed or separated
COPD may also be triggered by environmental pollutants, including room fresheners and herbicides. (Related: Study: Using Tylenol regularly can cause asthma and COPD.)
Herbs that can help remedy COPD
Aside from bai bu, you can also improve the function of your lungs with these herbs:
- Peppermint – This herb contains menthol that relaxes the muscles in the respiratory tract.
- Oregano – Contains carvacrol and rosmarinic acid that act as decongestants. These compounds also decrease the levels of histamines in the body, making it great for people prone to allergies.
- Turmeric – This can reduce inflammation in the lungs.
Read more articles on different types of Asian medicine at ChineseMedicine.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, bai bu, Chronic lower respiratory disease, COPD, herbal medicine, Herbs, lung function, lung health, natural cures, natural remedies, Natural Treatments, Naturopathy, Radix Stemonae, TCM, traditional Chinese medicine