Japanese study confirms vitamin D reduces cancer risk
04/15/2018 / By Michelle Simmons
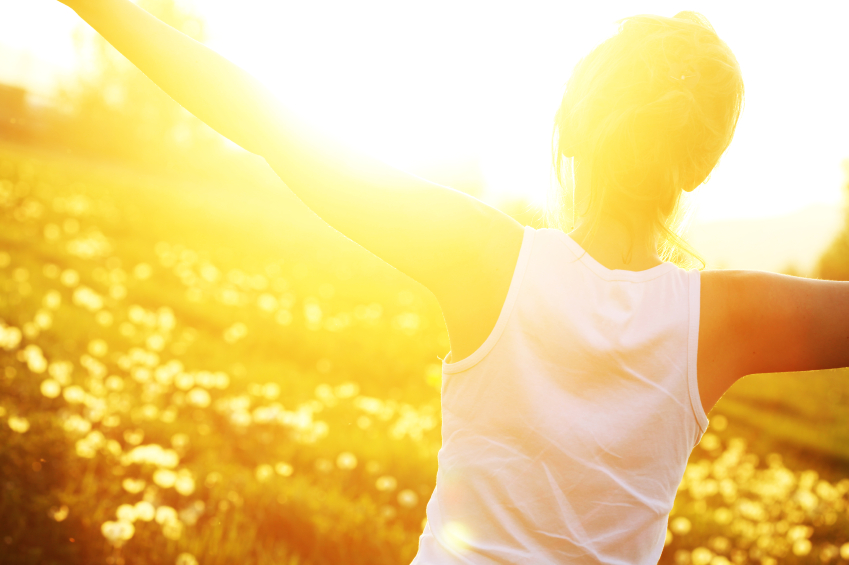

Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that is good for the health, and scientists continue to explore its other health benefits. In fact, a new study found that vitamin D reduces the risk of cancers. The large Japanese cohort study, published in the BMJ, aimed to determine whether vitamin D was associated with the risk of total cancer and certain cancers.
The researchers conducted the study using data of 33,736 participants from the Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective (JPHC) Study. The participants were aged between 40 and 69 years. At the beginning of the study, they provided detailed information on their medical history, diet, and lifestyle. Their blood samples were also taken to measure vitamin D levels.
Then, the researchers divided the participants into four groups, depending on their levels of vitamin D. After that, they observed the participants for an average of 16 years, in which they recorded more than 3,300 new cases of cancer. The study also included 4,044 randomly selected sub-cohort participants.
After cancer risk factors, such as age, weight, physical activity levels, smoking, alcohol consumption, and diet, were considered, the researchers found that participants with a higher level of vitamin D had a 20 to 25 percent lower risk for all cancers. For liver cancer, they showed a 30 to 55 percent lower risk of cancer, and the association was more evident in men than in women. In addition, they found that vitamin D levels lower the risk for pre-menopausal breast cancer, but not for prostate and lung cancer.
Furthermore, they observed a ceiling effect for total cancer risk, which suggested that no further benefit would be provided beyond a certain vitamin D blood concentration. However, they failed to determine the optimal vitamin D concentration that reduced the risk of cancer.
“We observed that a higher circulating concentration of vitamin D was associated with a lower risk of subsequent cancer in a large Japanese population. Our findings support the hypothesis that vitamin D may confer protection against the risk of cancer,” said Sanjeev Budhathoki, first author of the study.
Ways to get your daily vitamin D needs
Vitamin D is especially good for the bones. Studies also suggested that it can help prevent colds and fight depression. Thus, it is important to get enough vitamin D. (Related: Are you getting enough vitamin D? If you don’t take magnesium, you may not be absorbing your “D”)
Here are some ways to get your daily vitamin D needs:
- Get exposed to sunlight – Vitamin D is synthesized when the skin is exposed to sunlight. Getting around 20 to 25 minutes of sunlight exposure is helpful, but too much of it can increase the risk of cancer.
- Eat foods rich in vitamin D – If you are unable to get exposed to sunlight, especially during winter, get vitamin D from fatty fish, such as salmon, trout, mackerel, tuna, and eel. Fatty fish is not only a good source of the vitamin but also of the heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids. Other foods that are good sources of vitamin D include beef liver, cod liver oil, egg yolks, fortified milk, and fortified cereals.
- Take vitamin D supplements – Vitamin D can also be obtained from supplements. However, you must only take a proper daily dosage of these supplements. This is because too much vitamin D can be harmful. The safe upper limit of vitamin D per day for people aged nine and over is 4,000 IU, which includes all sources – sun, food, and supplements.
Read more news stories and studies on how to prevent cancer at Prevention.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: cancer, cancer risk, Liver cancer, nutrients, research, sun, sunlight, vitamin D, vitamins